Understanding Fiber Patch Cord Types: A Complete Guide for Network Professionals
Introduction
In today’s high-speed data transmission era, fiber optic patch cords have become essential components in telecommunication networks, data centers, and enterprise cabling systems. The right fiber patch cord not only ensures optimal performance but also minimizes signal loss, reduces downtime, and supports future scalability.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore different fiber patch cord types, their features, applications, and how to choose the right one for your project. Whether you are setting up an LC to LC patch cord connection for a small office or integrating an LC to LC multimode fiber patch cord in a large-scale network, this article will give you the insights you need.
1. What is a Fiber Optic Patch Cord?
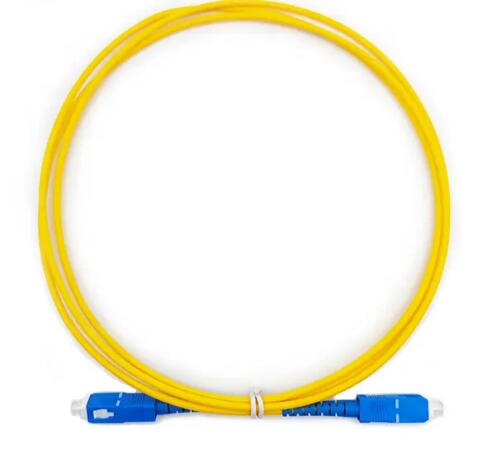
A fiber optic patch cord—also known as a fiber jumper—is a fiber cable terminated with connectors on both ends. These connectors allow quick connection between optical equipment such as switches, patch panels, optical transceivers, and distribution boxes.
Key functions of a fiber patch cord:
Connect different network devices.
Provide flexible cabling in telecom rooms and data centers.
Enable easy troubleshooting and network reconfiguration.
2. Key Components of a Fiber Patch Cord
Every fiber optic patch cord consists of the following:
Fiber Core – Transmits optical signals. Available in single-mode or multimode.
Cladding – Maintains the integrity of the light within the core.
Buffer Coating – Protects the fiber from physical damage.
Outer Jacket – Adds durability and environmental protection.
Connectors – Examples include LC, SC, ST, FC.
3. Fiber Patch Cord Types
When we talk about fiber patch cord types, they can be categorized based on:
Mode (Single-mode vs. Multimode)
Connector type (LC, SC, ST, FC, MTP/MPO)
Polish type (UPC, APC)
Cable structure (Simplex, Duplex, Armored, Uniboot)
3.1 Single-Mode Fiber Patch Cord
Core size: ~9 μm
Transmission distance: Long-range (up to 100 km)
Color code: Yellow
Applications: Long-haul telecom, metro networks, and FTTH deployments.
3.2 Multimode Fiber Patch Cord
Core sizes: 50 μm or 62.5 μm
Transmission distance: Short-range (up to 2 km)
Color codes: Orange (OM1/OM2), Aqua (OM3/OM4), Violet (OM4+)
Applications: Data centers, LAN, campus networks.

4. Common Connector Types
4.1 LC Connector
The LC to LC patch cord is one of the most popular options for high-density applications.
Small form factor
Push-pull mechanism
Ideal for 10G/40G/100G connections
4.2 SC Connector
Square shape with snap-in connection
Widely used in telecom closets
4.3 ST Connector
Bayonet-style twist lock
Older but still found in legacy systems
4.4 FC Connector
Screw-type connection for secure fit
Mostly used in industrial or high-vibration environments
5. LC to LC Patch Cord Explained
An LC to LC patch cord features LC connectors on both ends, ensuring low insertion loss and high return loss.
Available in:
Single-mode LC to LC patch cord
Multimode LC to LC patch cord
LC to LC uniboot design for reduced cabling footprint
6. LC to LC Multimode Fiber Patch Cord
The LC to LC multimode fiber patch cord is specifically designed for high-speed, short-distance data transmission.
Supports 10G, 40G, and even 100G Ethernet
Commonly used in server-to-switch connections
Available in OM3, OM4, OM5 standards

7. Specialty Fiber Patch Cord Types
Beyond standard options, the market offers:
Armored fiber patch cords – Enhanced durability against mechanical stress.
Bend-insensitive fiber patch cords – Designed to maintain performance in tight bends.
MTP/MPO patch cords – High-fiber-count cables for parallel optics.
8. Fiber Patch Cord Polish Types
UPC (Ultra Physical Contact) – Lower insertion loss, used in digital systems.
APC (Angled Physical Contact) – Best for CATV and high-precision systems with low back reflection.
9. How to Choose the Right Fiber Patch Cord
When selecting among various fiber patch cord types, consider:
Application environment – Indoor, outdoor, harsh conditions.
Transmission distance – Single-mode for long, multimode for short.
Connector compatibility – LC, SC, ST, or MPO.
Polish type – UPC vs. APC.
Cable structure – Simplex, duplex, armored.
10. Installation & Maintenance Tips
Avoid excessive bending of cables.
Keep connectors clean with fiber cleaning tools.
Label each fiber optic patch cord for easy troubleshooting.
11. Future Trends in Fiber Patch Cords
Higher density LC uniboot designs for space-saving data centers.
OM5 wideband multimode fiber for optimized wavelength multiplexing.
Pre-terminated fiber solutions for faster deployment.
Conclusion
Choosing the right fiber optic patch cord is vital for ensuring network reliability and performance. Whether you opt for a LC to LC patch cord for high-density connectivity or a LC to LC multimode fiber patch cord for data center links, understanding fiber patch cord types allows you to design a network that meets both current and future demands.