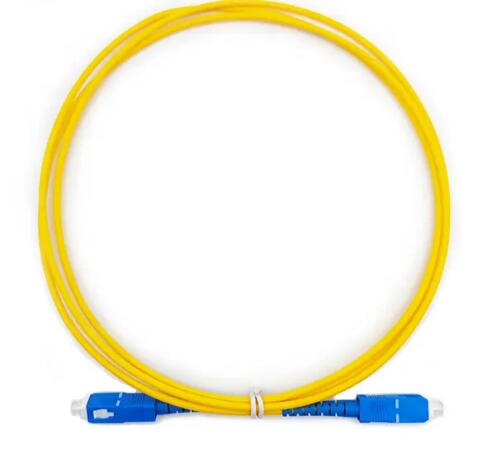
In the world of modern networking and telecommunications, fiber optic patch cords are essential components that ensure fast, reliable, and efficient data transmission. Whether you’re managing a data center, building a telecom system, or installing FTTH (Fiber to the Home) networks, understanding patch cords is key to system performance.
In this guide, we’ll cover what a fiber optic patch cord is, how it works, the different types available, and how to choose the right one for your project.
🔍 What Is a Fiber Optic Patch Cord?
A fiber optic patch cord, also known as a fiber jumper or patch cable, is a length of fiber optic cable with connectors on both ends. It’s used to connect devices to each other in a fiber optic network, such as connecting optical transceivers, patch panels, distribution boxes, or media converters.
Patch cords play a critical role in high-speed data transmission by ensuring minimal signal loss, low insertion loss, and consistent connectivity between network points.

📦 Components of a Patch Cord
Fiber Cable
Single Mode (SM): For long-distance, high-bandwidth connections
Multimode (MM): For shorter-distance, high-speed data transmission
Connectors
Common types include:SC/UPC, SC/APC
LC/UPC, LC/APC
FC, ST, E2000
These connectors determine the interface compatibility and optical performance.
Jacket Material
PVC, LSZH, OFNP: Depending on installation environment (indoor/outdoor, plenum-rated, flame-retardant)
🧵 Types of Fiber Optic Patch Cords
Fiber patch cords can be categorized by mode, structure, and connector types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Simplex | One fiber, one connector on each end |
| Duplex | Two fibers, used for bi-directional data |
| Single Mode | Yellow cable, long-range communication |
| Multimode OM1/OM2/OM3/OM4 | Orange/aqua cable, short-distance high speed |
| Hybrid Patch Cord | Two different connectors (e.g. SC to LC) |
| Armored Patch Cord | With steel tubing for protection |
🔧 Common Uses of Patch Cords
FTTH (Fiber to the Home) networks
Data centers and enterprise networks
Telecommunication base stations
Connecting optical distribution frames (ODF)
Linking fiber patch panels and distribution boxes
。
✅ How to Choose the Right Patch Cord
When selecting a patch cord, consider the following:
Connector Type: Match with your equipment ports (e.g. SC/UPC, LC/APC).
Cable Type: Choose single mode for long-distance, multimode for short.
Length: Custom or standard lengths available (1m, 3m, 5m, 10m, etc.).
Jacket Rating: LSZH for safety in buildings, armored for harsh environments.
Insertion Loss and Return Loss: Lower values mean better performance.
。
🛠️ Patch Cord vs Patch Panel vs Distribution Box
While patch cords are the connection cables, they work alongside:
Patch Panels: Organize and manage fiber terminations
Distribution Boxes: Protect and split fiber cables, often housing PLC splitters for FTTH applications
These components form the foundation of a well-structured and scalable fiber optic network.
💡 Maintenance Tips
Keep connectors clean and dust-free
Avoid bending cables beyond their minimum bend radius
Use proper labeling and cable management in patch panels
Test with a visual fault locator (VFL) or optical power meter if signal issues occur
📈 Conclusion
A fiber optic patch cord might look simple, but it’s a critical link in high-speed data transmission. Choosing the right type and quality ensures your network performs reliably — whether it’s for telecom, enterprise IT, or fiber-to-home connections.
If you’re looking for high-performance patch cords such as SC/UPC, LC/APC jumpers, simplex or duplex, or custom-length options, our factory offers OEM and bulk supply solutions tailored for your project needs.
📞 Need Help Choosing the Right Patch Cord?
Contact us today to get a quote or request a free sample for testing.